Army Gd
“Rise to the Challenge with Army GD: Build Strength, Discipline, and Courage, And Serve the Nation with Pride.”
“Looking for the best Army coaching near you? We offer comprehensive Army Bharti coaching for GD, open Bharti, and more. Find classes near you and prepare for success!”
General Duty (GD) soldiers form the backbone of the Indian Army. They are responsible for various tasks, including patrolling, guarding, and participating in combat operations. The recruitment process for GD soldiers involves several stages, including physical fitness tests, medical examinations, and written tests. Here is an overview of the process
Eligibility Criteria
To be eligible for GD soldier recruitment, candidates must meet certain criteria. These criteria may include age limits (usually between 17.5 and 21 years), educational qualifications (usually 10th or 12th pass), and physical fitness standards.
Soldier Technical, Clerk, Store Keeper, Tradesmen: Generally, candidates should be between 17.5 and 23 years old.
Officers (NDA, CDS): Age limits vary; for NDA, candidates should be between 16.5 and 19.5 years old. For CDS, the age limit is generally 19 to 24 years.
Online Registration
Candidates must first register online on the official Indian Army website or through the Army Recruitment Rally (ARR) website. They will need to provide personal and educational details during the registration process.
To begin your journey towards joining the Indian Army as a General Duty (GD) soldier, the first step is to complete the online registration process. Start by visiting the official Indian Army recruitment website at joinindianarmy.nic.in. On the homepage, create an account by providing your basic details, including your name, email ID, and phone number. After successfully registering, log in using your credentials and navigate to the “Apply Online” section. Select the “Soldier General Duty” category and fill out the application form with accurate personal and educational information. Ensure that you upload all required documents,

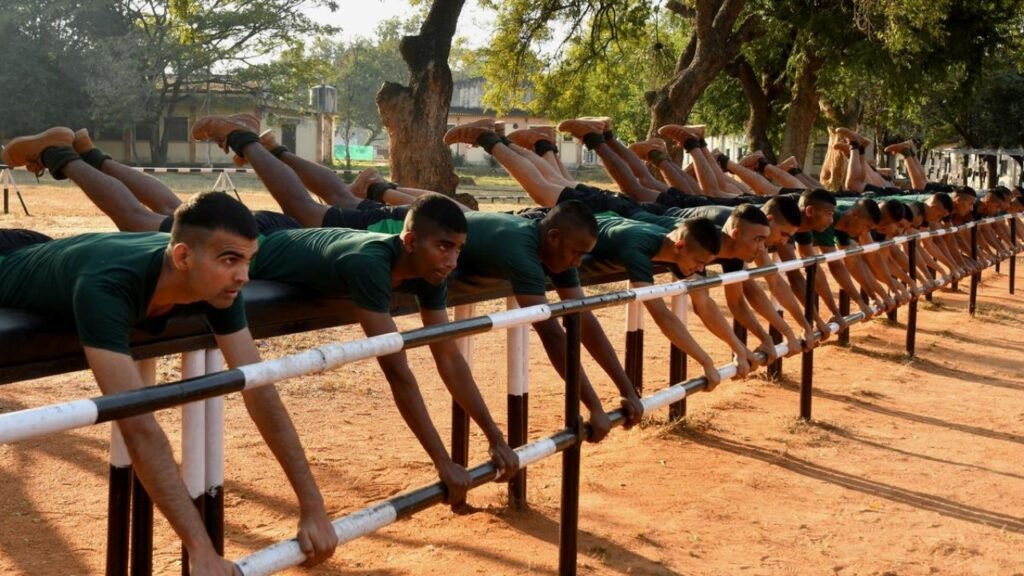
Physical Fitness Tests
Candidates who pass the online registration stage will be called for physical fitness tests. These tests may include a 1.6-kilometer run, pull-ups, and other exercises to assess physical endurance and strength..
Purpose: This test evaluates cardiovascular endurance and overall stamina.
Reps: Candidates must perform a minimum of 10 pull-ups. Each pull-up should be done with a full range of motion, from hanging fully to chin above the bar.
Purpose: This test assesses upper body strength and endurance.

Medical Examination
Candidates who pass the physical fitness tests will undergo a medical examination to ensure they meet the medical standards set by the Indian Army.
General Health Check-Up
Objective: Assess overall health and identify any medical conditions that may disqualify a candidate.
Components: Includes a general physical examination where doctors check for vital signs, body mass index (BMI), and overall health.
Vision and Hearing Tests
Vision: Candidates must have correctable vision to 6/6 in each eye, with or without glasses. There are also specific standards for color vision and night vision.

Written Test
Candidates who pass the medical examination will be eligible to appear for a written test. The written test typically covers topics such as general knowledge, mathematics, and reasoning.
Test Structure
Objective Type: The written test typically consists of multiple-choice questions (MCQs).
Duration: The test usually lasts for 1 to 2 hours
General Knowledge (GK): Questions related to current affairs, history, geography, culture, and significant national and international events.

Merit List and Selection
Based on the performance in the physical fitness tests, medical examination, and written test, a merit list will be prepared. Candidates who are selected will be called for further training and induction into the Indian Army.
Merit List Preparation
Written Test Scores: The primary criterion for the merit list is the scores obtained in the written test. Candidates are ranked based on their performance, with higher scores leading to a higher rank.
Physical Fitness Test (PFT): Candidates who pass the Physical Fitness Test are also considered. PFT scores contribute to the overall assessment but are not the sole determining factor.

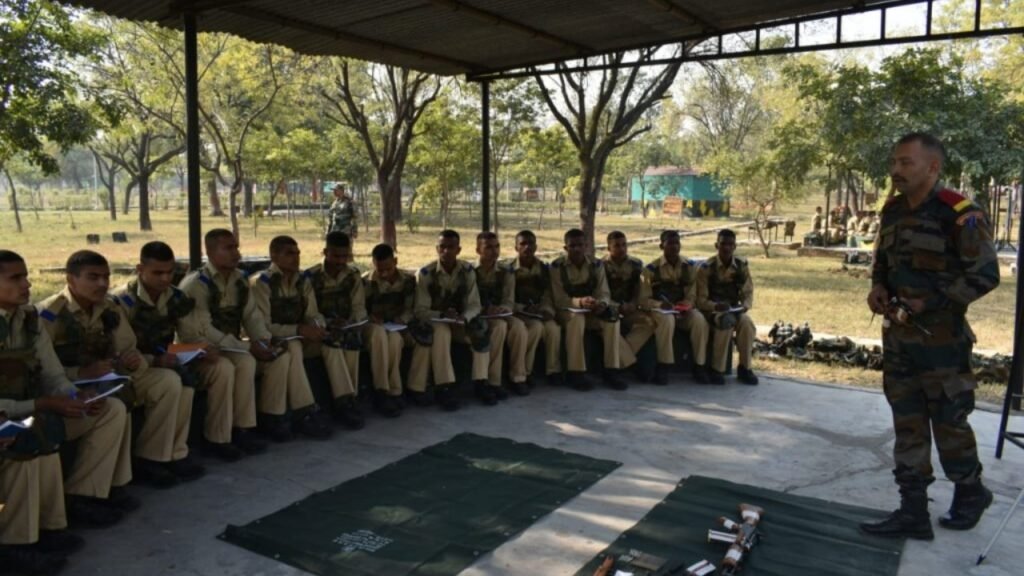
Training
Selected candidates will undergo training at one of the Indian Army’s training centers. The training will cover various aspects of military life, including physical fitness, weapons training, and discipline.
Basic Training
Duration: The basic training typically lasts around 9 to 12 months, depending on the specific requirements and the training center.
Fitness Regimen: Includes running, strength training, endurance drills, and obstacle courses to build physical stamina and combat readiness.
Handling Firearms: Training in the use of standard-issue weapons, including rifles and machine guns.

It’s important to note that the recruitment process may vary slightly depending on the specific recruitment rally or region. Candidates should carefully read the official recruitment notifications and follow the instructions provided.
Please remember to check the official Indian Army website or contact a recruitment office for the most up-to-date information on the GD soldier recruitment process.
